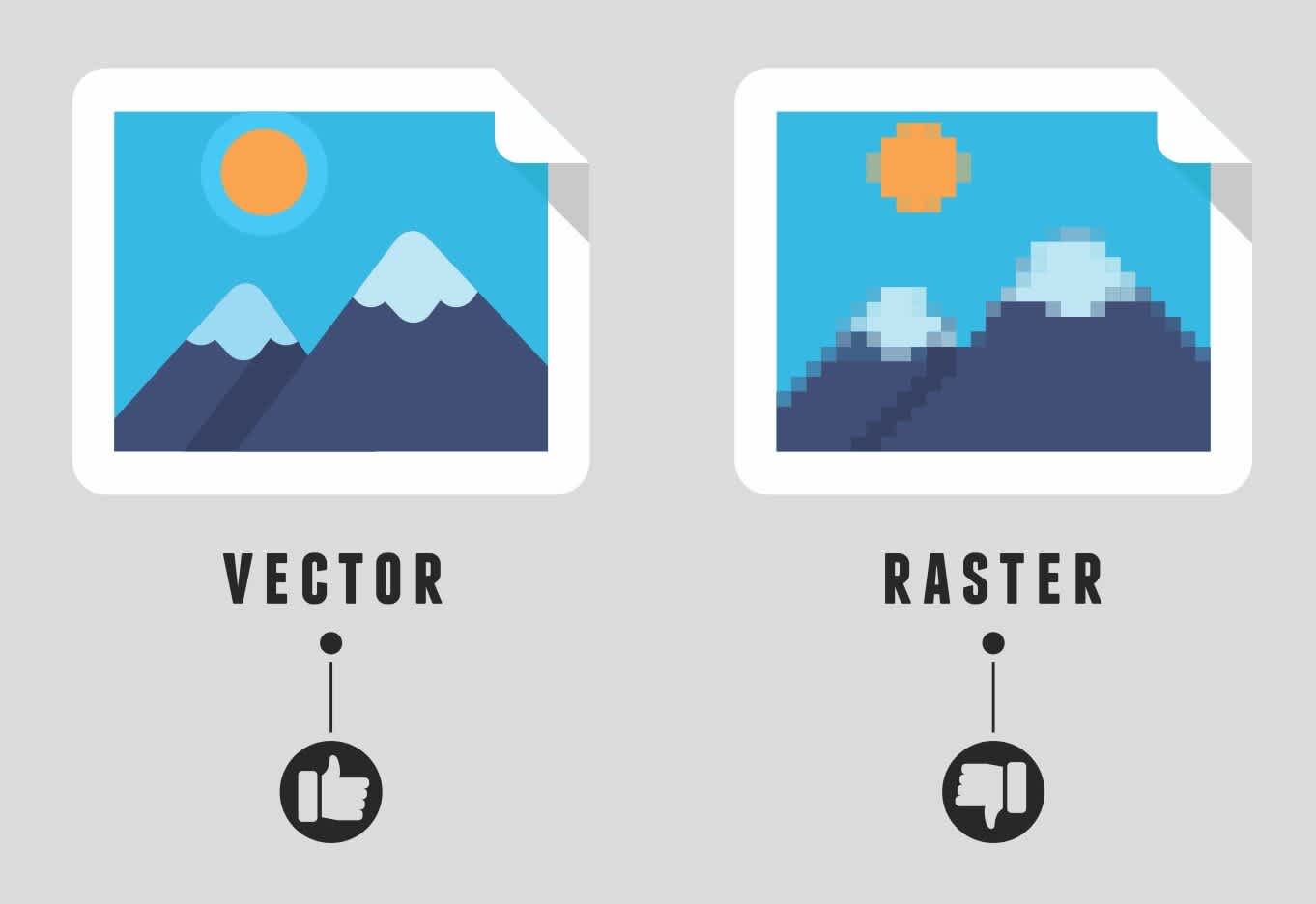
In the burgeoning digital media landscape, understanding the difference between vector vs. raster graphics is essential. These two forms of images are utilized everywhere from web design, digital marketing, and graphic design to photography and television. In this in-depth feature, we will delve into the intricacies of these two types to help you understand the best application for each.
What Are Raster Graphics?
Raster graphics, also known as bitmap graphics, consist of pixel-based images. Every image is composed of millions of tiny squares, colloquially known as pixels. Together, they form a complete image. Most digital photos you come across online are raster graphics.
The Composition of Raster Graphics
A raster image's quality is contingent on its resolution. More pixels translate to a higher quality image and, ergo, a larger file size. One significant aspect of raster images is that they are resolution-dependent. It means when you try to enlarge a bitmap image beyond its original resolution, it begins to lose quality and appear pixelated or blurry.
Popular raster file formats include:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
- BMP (Bitmap Image File)
With photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop, you can manipulate raster images to deliver vivid and detailed pictures.
What Are Vector Graphics?
When discussing vector vs. raster graphics, understanding vector graphics is key. Unlike raster graphics, vector images are resolution-independent and are based on mathematical formulas that create shapes, curves, lines, and text. As a result, they retain their quality when scaled to different sizes.
The Composition of Vector Graphics
A vector image can be described as a series of points connected by lines or curves to form a complete image. Due to their mathematical basis, vector images retain their sharpness and clarity at any size or resolution. This quality makes them ideal for company logos, typography, and graphic design.
Common vector file formats include:
- AI (Adobe Illustrator)
- EPS (Encapsulated PostScript)
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
- PDF (Portable Document Format)
With software like Adobe Illustrator and Corel Draw, you can create and manipulate vector graphics.
The Significance of Vector vs. Raster Graphics
Let's delve deeper into the significance of this comparison.
Vector Graphics for Scalability and Adaptability
The most prominent advantage of vector graphics is their scalability. You can resize vector graphics to almost any extent without worrying about the loss of quality. This feature makes vector graphics ideal for brand logos, which need to be adapted across various platforms and sizes. If clarity and scalability are your top priorities, vector graphics are your best bet.
Frequently Asked Questions about Vector Vs. Raster Graphics
What is a Vector Graphic?
Vector graphics are composed of paths or strokes, which are defined by a start and end point, along with other points, curves, and angles along the way. A path can be a line, a square, a triangle, or a curvy shape. These paths can be used to create simple drawings or complex diagrams. Unlike raster graphics, vector graphics are not based on pixel patterns, but instead use mathematical formulas to draw lines and curves that can be combined to create an image from geometric objects such as circles and polygons.
What is the Key Difference Between Vector and Raster Graphics?
The primary difference between vector and raster graphics is that raster graphics are composed of pixels, while vector graphics are composed of paths. A raster graphic, such as a gif or jpeg, is an array of pixels of various colours, which together form an image. A vector graphic, such as an .eps file or Adobe Illustrator file, is composed of paths, or lines, that are either straight or curved. The data file for a vector image contains the points where the paths start and end, how much the paths curve, and the colours that either border or fill the paths.
Are there Any Notable Differences in File Sizes Between Vector and Raster Graphics?
Yes, there are significant differences in file sizes between vector and raster graphics. Raster file sizes are significantly larger because they contain a fixed number of pixels and much more data. Vector files, on the other hand, are smaller because they contain mathematical descriptions of an image rather than actual image data.
Can I Convert Raster Graphics into Vector Graphics and Vice Versa?
Yes, raster graphics can be converted into vector graphics with the help of specific software, such as Adobe Illustrator. Keep in mind that the accuracy of a converted image strongly depends on the quality of the original raster graphic. High resolution with clear, clean lines works best.
On the other hand, converting a vector image to a raster graphic is quite simple and can be done in almost all graphic programs.
When Should I Use Raster Graphics?
Raster graphics are best suited for non-line art images; specifically digitized photographs, scanned artwork, or detailed graphics. Non-line art images are best represented in raster form because these typically include subtle transitions, undefined lines and shapes, and a full spectrum of colour.
When Should I Use Vector Graphics?
Vector graphics are ideal for images that frequently need resizing. Logos, icons, and other types of drawings are often in vector format because these graphics can be resized easily without losing quality. Vector images are also very flexible. They can be converted to raster files when needed without losing the original vector file data.
How Do Resolution and Scaling Affect Vector and Raster Graphics?
Raster graphics become "blocky" and "pixelated" if they are enlarged beyond their highest resolution. However, vector graphics maintain the clarity and sharpness no matter how much you enlarge them, because they are mathematically described.
Are Vector Graphics Suitable for Online Use?
Yes, vector graphics can be used online. Actually, it’s becoming more common, especially with platforms that support SVG file format, like HTML5.
Pros of Vector Graphics
Flexibility in Scaling
No Loss in Resolution
Vector graphics maintain their high-quality look no matter how you manipulate them. Be it scaling or rotating, they keep their visual integrity with no degradation in quality. This is possible because vector graphics use mathematical formulas to construct the image.
Infinite Zoom
With vector graphics, you don’t need to worry about pixilation when zooming in. This is due to the mathematical equations that detail where the edges of the shapes lie, so they can be zoomed infinitely with no degradation in quality.
Small File Sizes
Vector files take up less storage space compared to raster graphics. This is an advantage when trying to keep a website loading time quick or save storage space.
Easy to Edit
You can easily modify vector graphics without impact on their quality. You can change colors, resize lines, and add or remove features effortlessly. This makes vector graphics an ideal option for logos, icons, and other designs that often require modifications.
Cons of Vector Graphics
Not Great for Complex Images
Vector graphics are ideal for creating simple, clean designs with solid colors. But they might not be the best option for more complex, multi-colored graphics like a realistic photograph.
Need Special Software
To create and edit vector graphics, you need specialized software like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW. These come with a steep learning curve, making it tough for non-designers to work with vector graphics.
Not Web Friendly
Most web browsers cannot directly display vector graphics. They need to be converted into a rasterized format like .jpeg or .png–consequently, losing all the advantages of vector format.
Pros of Raster Graphics
Excellent for Detailed Images
Raster graphics excel in the department of creating digital paintings, digitized photographs, and any image with complex color gradients. The color depth and complexity in raster images are much higher than what is possible with vector graphics.
Variety of Editing Options
Raster graphics can be edited pixel-by-pixel. This versatility allows for detailed image editing such as retouching, color correction, and adding complex special effects.
Web Friendly
Raster images can easily be displayed across various digital platforms and devices. This includes websites, since formats like .jpeg and .png are widespread and universally supported.
Cons of Raster Graphics
Not Scalable
One of the main drawbacks of raster graphics is that they do not scale well. When you resize a raster image, you either cram the pixels closer together or spread them farther apart. This causes the image to become fuzzy or pixelated, resulting in a loss of clarity and quality.
Large File Sizes
Due to the amount of data needed to detail each pixel, raster file sizes can get quite large, especially for high-resolution images. This can lead to increased loading time on websites and a drain on storage resources.
Difficult to Edit without Quality Loss
Unlike vector graphics, editing raster images may decrease the quality, especially if there are many revisions. The more you manipulate a raster image, the less sharp it becomes.
So, when deciding between vector or raster graphics, you need to consider factors like the complexity of the image, how much you will need to modify it, your storage capabilities, and how you plan to display it.
Summary
So there you have it, a rundown of what "Vector vs. raster graphics" entails. When you chat with your tech-savvy friends, you can now confidently explain the key differences. Remember, vector graphics are best for detailed and scalable designs like logos and prints. They're defined by mathematical equations, which means they maintain their crisp, high-quality look no matter how much you zoom in or out.
On the flip side, raster graphics are the go-to for complex, multi-colored images and photographs. They're made up of individual pixels, each with a specific shade or color. This results in highly detailed images, but it can cause blurriness when you resize them. So, when deciding between vector and raster graphics, your choice should depend on your project requirements.
With all this info, you can make wise decisions that make your designing work easier and greatly improve your outcomes. "Vector vs. raster graphics" isn't just a phrase thrown around in designer circles, it can also be a game-changer for those of you looking to create some impressive designs. Keep these points in mind and you'll be golden. Pretty cool, eh?
About WebPerfex;
WebPerfex is a lively team of talented professionals based in the heart of Roseville, CA. We're passionate about helping businesses achieve their digital aspirations. We truly believe that a solid online presence can make a world of difference to any business targeting growth, and have been helping clients bring in more traffic, leads, and sales since 2014. We're all about strategy, creativity and technological innovation—web designing, digital marketing, search engine optimization, you name it—WebPerfex has got you covered! If you're all about very chill vibes and high work ethics, you've found the right place! We can't wait to craft a phenomenal digital experience for you!